Converting Fractions Lesson
| Materials/Resources: Blackboard, Chalk, Micrometers, Calculators, Precision parts, handouts | Independent Practice (Assignments): Worksheet | ||
| Pennsylvania Standards: 1. 3.6.10.C- Apply physical technologies of structural design, analysis and engineering, personnel relations, financial affairs, structural production, marketing, research and design to real world problems. 2. 3.7.10. B- Apply appropriate instruments and apparatus to examine a variety of objects and processes. |
|||
| Performance Indicators The student will: 1. Identify the correlation between measurement technology and math through the use of fractions and converting numbers into decimals. 2. Utilize proper measurement techniques with a micrometer to measure specific, precision items. |
|||
| Instructional Strategies: Lecture Demonstration Audio-video presentation Student practice Brainstorming Field trip Guest speaker Room maintenance Peer tutoring Experimentation Class discussion Note taking Cooperative Learning Other |
Assessment Strategies: Teacher-made tests: After the students practice converting fractions and using a micrometer, students will take a test on the subject matter. Demonstrations: students will demonstrate to the teacher how to accurately measure an object using a micrometer. Laboratory experiments Oral presentations Panel discussions Charts and other graphics Teacher Observations: Teacher will observe students measuring various precision parts. Homework assignments Computer lab participation Notebooks Portfolios Anecdotal records Student self-reflections Research projects Other: Active participation in converting fractions to decimals and using a micrometer to measure various precision objects. |
Adaptations: Modified assignments Cooperative learning Modified expectations Tests read orally Task analysis Acceleration Computer reinforcement Preferential seating Repeated practice Other: Teacher Notes, Speak loudly for all students to hear, Use of proximity, Obey all IEP’s, SA’s and BMP’s Enrichment: Expanded project options Student selected research/project Other |
|
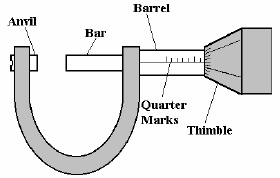
| Detailed Lesson Outline: 1. Start with review of the parts of a fraction of the inch 2. When working with fractions, the top number is the numerator and the bottom number is the denominator. 3. How do we convert fractions into decimals? a. Reduce fraction to lowest terms b. Divide numerator by denominator, ex: 1/8=.125 c. All decimals in this class will be wrote out to 3 or 4 decimal places 4. Lead to each fraction of an inch on a ruler or tape measure can be converted into a decimal. a. 1”=1.000 b. ½” =.500 c. ¼”=.250 d. 1/8”=.125 e. 1/16”=.0625 f. 1/32”=.03125 5. By knowing the basic decimals for the standard fractions of an inch, they can apply them to figure out other fractions. 6. Convert 3/8 into decimal form: 3*.125=.375 (.125 comes from 1/8) 7. Convert 7/16 into decimal form: 7*.0625=.4375 8. Convert .625 to fraction: .5+.125=.625 1/2 + 1/8 4/8 + 1/8=5/8 .5 and .125 come from chart above 9. Check understanding of converting. 10. Complete more examples of both as needed. 11. Draw and label a micrometer on the blackboard and pass out micrometer handout.
11. Explain parts of micrometer and show how to
read |
Introduction: Once students are
seated, bring out a box of precision parts like pistons, valves, pipe fittings, various engine parts to engage students. Pass around parts while asking students how these parts are measured and what are the dimensions measured in? Then led into discussion on how we can accurately measure these parts down to a thousandth of an inch. Questions to Ask: What type of dimensions are most technical or CAD drawings done in? Where in today’s society do we use decimals to measure? Why? What applications require the use of measuring with a micrometer in the subsystems on technology? What other ways or methods can we use to convert fractions to decimals or decimals to fractions? Why are fractions not used as much on drawings and blueprints anymore? Conclusion: • Go over worksheet to verify student comprehension • Pick out random fraction measurements and have students convert them to decimals for review. • Take any other questions students might have regarding decimals and micrometer measurement and answer them to further review lesson. • Inform students there will be test on this material in two days. |
||